Metal detectors are required in many industries, like security, and they can provide hours of
recreational entertainment as a pastime. Each metal detector must be calibrated to be sensitive to
the kind of material that the machine needs to detect.
Metal detector calibration is a process that sets the metal detector to a specific sensitivity.
Depending on the intended use of the metal detector, different sensitivities must be
achieved for each machine to detect the desired size and type of metal or metal
contaminant.
Each detector must be calibrated differently, and it is good to know the different processes of
calibration, validation, and audit for each machine. It is crucial that the metal detector’s
sensitivity be correct for certain industries, like food preparation, pharmaceuticals, and textile
production.
What Is Metal Detector Calibration?
Metal detector calibration is, quite simply, the process of setting a metal detector to the desired
sensitivity. The sensitivity of a metal detector determines the machine’s ability to detect specific
types and sizes of metals.
The different purposes and environments that metal detectors operate in require calibration to
different sensitivities and to discriminate between metals. The size of the metal that a metal
detector will react to is determined by sensitivity. Most recreational metal detectors also have
discrimination settings that determine the types of metals to which it will react.
Other settings, like depth control and discrimination, are built into high-end recreational metal
detectors. These settings are pre-loaded so that, with the push of a button, the user can decide
which kinds of metals to which they want the detector to react to.
Another common setting on recreational metal detectors is for environmental factors. Many
recreational detectors will have settings that discriminate between iron-heavy soil, salty beaches,
and other environments.
These settings are designed to be simple to use and are accessible through the user interface of
the metal detector. Simply choose the environment into which you are taking the detector, and
the machine will discriminate for that kind of soil or environment.
Understanding Metal Detector Sensitivity
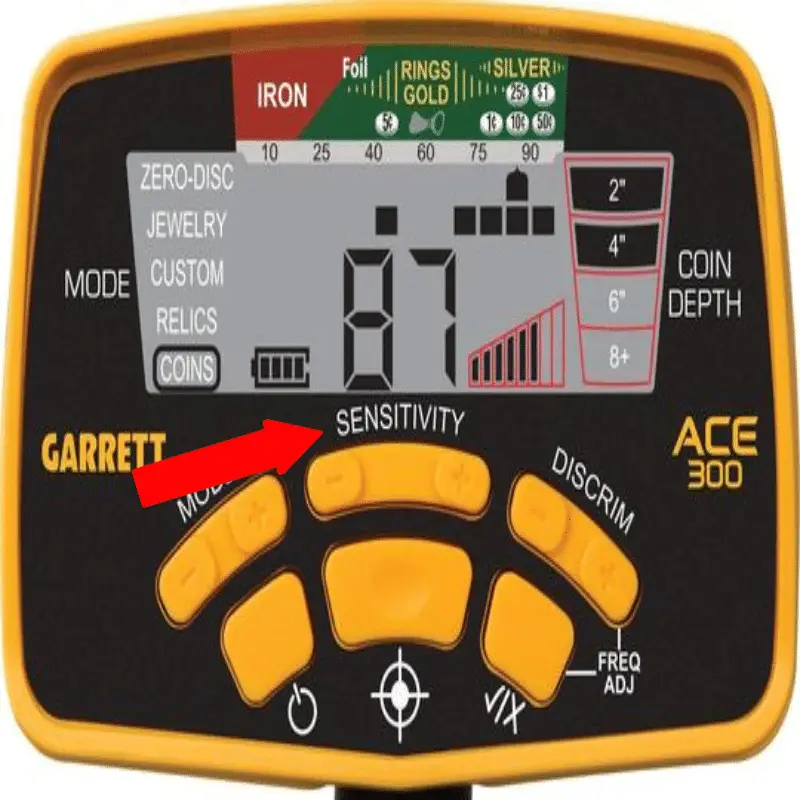

The higher the sensitivity, the smaller the pieces of metal a metal detector will detect. Detectors
can pick up ferrous, non-ferrous, aluminum, or stainless steel. Most detectors can be calibrated to
detect (or ignore) those types of metals.
Ferrous metals are the easiest to detect and, with high sensitivity, most machines will be able to
detect very small pieces of ferrous metals. Ferrous metals are generally magnetic and, since
metal detectors react to the magnetic field of metal, they are easier for the machine to detect.
Stainless steel is the most difficult to detect, and, as such, if you are trying to detect stainless
steel, you might need to calibrate the detector to very high sensitivity.
Generally, a metal detector’s sensitivity is determined by its ability to detect metal of a certain
diameter. Small changes in sensitivity can have a big impact on the size of metal pieces or
contaminants that a metal detector can detect.
Metal detectors that are used in industrial and security settings usually have high sensitivity so
that their alarms will sound when even the smallest piece of metal passes through.
Understanding Metal Detector Discrimination
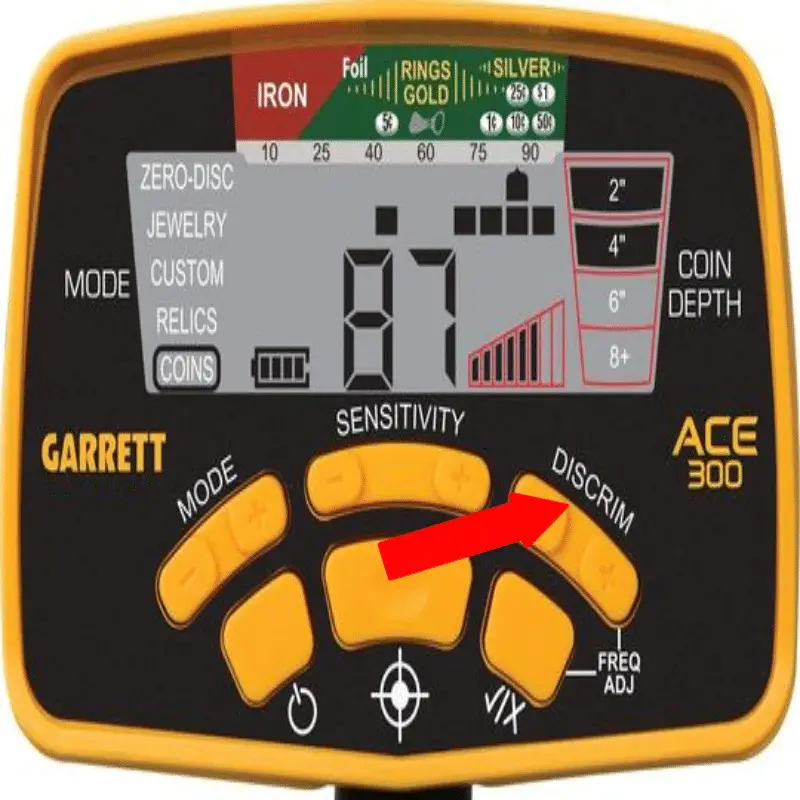

So what is discrimination in metal detecting?
Discrimination settings on metal detectors let the user or operator decide which metals to which
the detector reacts. Often, users will have good reason to set the metal detector to discriminate
for iron or aluminum so that those common metals aren’t found.
In industrial settings, metal detectors will sometimes need only to find a certain kind of metal
that is present in the work environment so that quality control workers can be sure that those
metals are not present in the products as before they are shipped out.
If an industry needs a metal detector to discriminate for certain metals, they will ask the
the manufacturer or the company that services their detector to set those discrimination parameters.
Walk-through metal detectors that are used for security are not calibrated to discriminate for
certain metals because the purposes of those are to detect any metal on the person that passes
through the detector.
Many recreational metal detectors also have easy-to-use discrimination settings. With a few
button clicks on the user interface, users can set the metal detector to discriminate for certain
metals. This is a handy feature in iron-rich areas to eliminate noise and chatter from the detector
and allow the user to find more valuable metals.
Other Calibration Factors
In addition to sensitivity and discrimination, the orientation of a metal detector will determine its
ability to detect a non-spherical piece of metal, such as a wire. The spherical diameter of wire
might be smaller than the detector’s sensitivity can detect, in some cases, and the orientation
effect can give the detector the ability to pick up on such pieces of metal.
If you are looking to install an industrial metal detector into your production facility, the
company that sells you the detector will calibrate the detector to your desired specifications.
They will work with you to ensure that the kinds, sizes, and shapes of metal that you need to
detect are picked up by the metal detector and activate the detector’s alarm.
There are different environmental factors that can also affect the detector’s performance. Some
recreational metal detectors have pre-loaded modes that can help to reduce the noise of a salty
beach or other environments, while factory metal detectors will have noise and vibration
immunity built-in to minimize the risk of electrical interference.
If you plan to use your metal detector on a salty beach or are aware that there is a lot of iron in
the area you will be using the metal detector, do research to make sure you buy a metal detector
that has features that allow you to calibrate and discriminate for those environmental factors.
How Metal Detectors Work
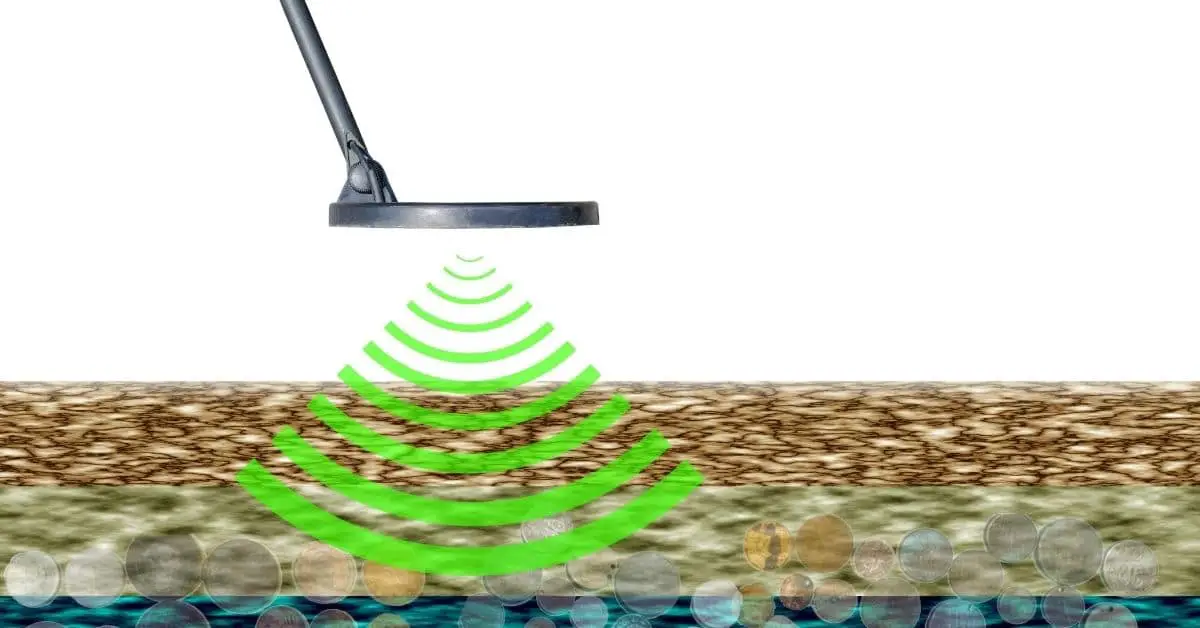
There are all different sorts of metal detectors for industrial use, security, and personal
recreational use, but they all operate using the same basic principles. Understanding how metal
detectors work will help you to know how to calibrate them and why calibration is important.
Every metal detector has a single coil or a set of coils. Those coils use electromagnetic induction
to detect the presence of metal. They produce an electromagnetic field that causes the metal
detector to sound an alarm when in contact with the magnetic field produced by metals.
This is how metal detectors can determine what type of metal it is detecting. Each metal’s
electromagnetic field is different, so metal detectors are programmed to recognize specific fields
as specific metals. A metal’s electromagnetic field is like a signature that is specific to that metal
or alloy.
Sensitivity settings increase or reduce the size of the magnetic field to which the detector will
react. Discrimination settings allow certain electromagnetic signatures to pass through without
alarm while it will react to others.
Large metal detectors, like those insecurity or food processing, are operated by a microchip that
is programmed for sensitivity, orientation, and discrimination. Recreational metal detectors are
also operated by microchips, but the user interface of each detector allows users to change the
programing whenever the need arises.
Digging Deeper: How Metal Detectors Work – A Comprehensive Guide
Industrial Metal Detectors
Metal detectors are common in many industries, such as wood processing, biofuel, recycling, and
aggregate industries. Corporations like Metal Detectors Inc. produce and service high-quality
metal detectors for industrial use.
Large industrial metal detectors are operated by a microchip that is programmed for sensitivity,
discrimination, and orientation. This is why it is almost always required to have a specialized
technician calibrate and validate industrial detectors.
Laborers in these industries will not be expected to calibrate these metal detectors. It is more
likely that a service technician from the company that produced the metal detector will calibrate
the metal detector to the desired discrimination and sensitivity when the detector is installed.
Corporations like Metal Detectors Inc. also offer servicing for their products. They will visit the
factory or production location regularly to service, repair, calibrate, and validate the metal
detectors that they produce. They utilize standards of pure metals at different sizes to validate
that the sensitivity and discrimination settings are working as required by the factory setting.
Examples of industrial metal detectors include those that sit atop conveyor belts. These are used
in the aggregate industry to ensure that only the materials that are desired are passing through the
detector and give laborers the ability to easily locate and pick out unwanted metals.
Wood mills also use large metal detectors to make sure that only wood is passing through.
Sometimes, large trees have metal shards in them that need to be removed before that wood can
be processed.
Securities Metal Detectors
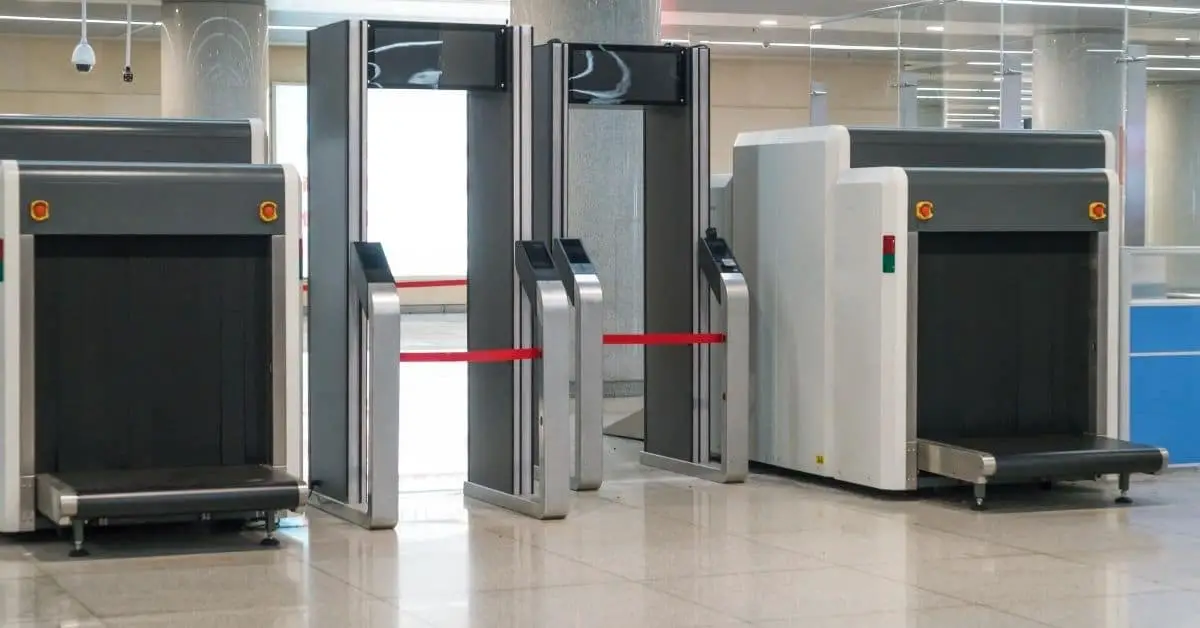

Anyone who has been through an airport is familiar with the large, walk-through metal detectors
that securities professionals utilize. These metal detectors are set to high sensitivity. You may
have noticed that they will pick up the smallest bit of metal, like earrings and other jewelry.
Most metal detectors rely on a single coil; walk-through metal detectors utilize two coils. A
current is sent through both coils through a process called pulse induction. The two coils send
pulses of electrical current between each other.
Each pulse lasts only about 30 microseconds, and walk-through detectors can emit hundreds of
pulses every second. When the pulse interacts with a metal of any kind, it detects the magnetic
field and the alarm on the detector sounds.
Protective Technologies International is one corporation that produces and services metal
detectors. They calibrate these detectors to high sensitivity and no discrimination so that any
metal on a person will be detected.
Many securities metal detectors now operate with digital technology, which allows the company
that produced the detector to constantly monitor and adjust the detector’s settings via an internet
connection. This ensures that, in a most crucial environment, the metal detectors are always
operating as they should.
Why Calibration Is Important

Whether using a metal detector for recreation or industrial purposes, calibration is important in
order to set the metal detector up to successfully detect the desired size of metal or type of metal.
Industrial
Proper calibration is crucial for industrial metal detectors and, while the manufacturer will
typically service and calibrate the detector for the client, it can be useful to know about how
sensitivity affects what will be detected.
Since foods and other goods are manufactured and produced using automated machinery, it is
possible that metal shavings or other machine parts get mixed up in the product. Proper
calibration is especially important for industrial applications of metal detectors in food
preparation and other factory production to ensure that no metal contaminants are present in the
product.
Regular calibration is important for all industries where metal detectors are used daily. If a metal
detector is malfunctioning and metal slips through undetected, it can cause costly damage to
machinery or unwanted metal might be shipped out with products.
Certain packaging materials and product characteristics can affect the sensitivity, and necessary
calibration, of a metal detector. It is important that industrial detectors are calibrated to the
proper specification so that the type and size of the metal contaminant in products are accurately
detected.
Security
Metal detector calibration is important in security settings for the alarm to sound if anyone tries
to enter a building or airplane with metal that is not allowed. For instance, metal detectors are
placed at the front of many government buildings so that no one can bring a weapon or other
dangerous metal object into the building.
Airports security requires a metal detector to ensure that no one is hiding anything dangerous
underneath close or elsewhere. These walk-through security metal detectors are calibrated to a
high degree of sensitivity so that the alarm sounds when even the smallest bits of metal is
passed through.
Additionally, schools now often have metal detectors at some entrances so that students and
visitors cannot enter the building with weapons or other dangerous metal objects. Calibration is
crucial in these environments so that everyone in the building is kept safe.
Recreational
Recreational metal detectors will usually have simple, straightforward sensitivity controls that
allow you to adjust the sensitivity and, consequently, the size of metal the detector will detect.
They will also sometimes allow users to eliminate the detection of certain kinds of metal or
automatically calibrate for certain environmental factors.
It is important to set follow the steps below to adjust the sensitivity of the metal detector so that
it sits in the right range to pick up on metals without producing excess noise. Many metal
detectors also have pre-loaded settings for discrimination. They might also have settings that
calibrate the metal detector for saltwater beaches, dense clay soil, and iron-heavy soil.
Since each model of metal detector is different, it is important to read the manual for your
detector to determine how you can access each of the settings for your detector.
The Difference Between Calibration, Validation, and Audits
While calibration sets the sensitivity for the size and types of metals to which a metal detector
reacts, validation and audits are designed to test that calibration. Validation is conducted
regularly in industrial or security settings in order to ensure that the metal detector is still
properly calibrated.
Validation and audits are conducted every day with industrial and securities metal detectors.
Each time the detector reacts to metal, that is a validation that the machine is still working
properly.
For recreational metal detectors, you can validate that the detector is working properly by setting
metals of different kinds on the ground and making sure that the user interface recognizes it as
the right type of metal. Adjusting sensitivity will determine the size of metal objects it picks up.
Recreational users can also validate that the discrimination settings on their detectors are
working properly by setting the detector to discriminate against something like iron and then
passing the detector slowly over a piece of iron to see if the detector reacts.
Calibrating Industrial & Securities Metal Detectors
As mentioned above, the corporations that produce metal detectors for industrial or securities
uses will perform an initial calibration. Those companies also usually offer servicing for the
machines that they produce.
Every metal detector is different. There are detectors that are designed for specific use in the
food production industry, textile manufacturing, milling, and many others. Walk-through metal
detectors are designed for securities applications.
The companies that service metal detectors will know how to access the control panel for each
machine. They will probably also have a device that is connected to the control panel that allows
sensitivity, discrimination, and orientation to be adjusted.
Before being sold to industries, metal detectors are calibrated and validated with cards of specific
types of metal. The process is rigorous to ensure that the detector was produced in the right way
and that it will function properly once it gets to the location where it will be used.
Factories that have a lot of different metal detectors for different conveyor belts or assembly
lines might hire a specialized metal detector technician to make sure that all of their detectors
function properly every day.
How To Calibrate A Recreational Metal Detector

Metal detectors that are put to use in industrial or securities settings are typically calibrated by
professionals and is often a service provided by the manufacturer that produced and sold each
detector. Calibration for recreational detectors can be conducted at home through a number of
steps and is different for each metal detector.
To calibrate a recreational metal detector, you will first want to become familiar with the settings
of that metal detector. If you have the manual that came with the detector, read that to understand
the different settings of your device.
Many recreational metal detector manufacturers also make their manuals available online, so you
might search for the manual that corresponds to the make and model of the metal detector that
you own if you don’t have access to the physical manual.
There are two standard functions of recreational metal detector calibration: sensitivity and
discrimination. Sensitivity, as mentioned above, controls the size of metals that will be detected,
and discrimination determines the types of metals that can be detected.
Some recreational detectors also have pre-loaded settings that allow the owner to calibrate for
certain environmental factors that might interfere with the detector’s performance. For example,
the saltwater on beaches can interfere with a metal detector and produce a lot of noise, but some
recreational detectors have settings that allow the detector to function as normal on a saltwater
beach.
Digging Deeper: Are Hobby Metal Detectors Safe?
Calibrating Recreational Metal Detectors
The goal of calibration is to find the narrow window of sensitivity that will allow you to detect
the metal properly without producing excess noise and chatter. Most metal detectors take large
batteries, such as 9-volt batteries, for power.
Before conducting a calibration routine, power the detector up and let it warm up for 5-10
minutes. This will ensure that the coil is operating at full capacity before you attempt a
calibration.
The basic calibration and validation method for recreational metal detectors is as follows:
ï‚· Find a large, flat area in your yard or driveway. Use the metal detector to search that area
and make sure no targets or contaminants are there. If they are, remove the source of
interference or find a different spot.
ï‚· Place a coin of each type and a piece of jewelry or other metal on the ground and use the
metal detector to see how it reacts. Proper detection requires slow, methodical
movements.
ï‚· You can determine the depth at which the metal detector will react by moving the coil
away from the objects. This isn’t quite accurate, but it will give you a general idea. The
detector will work better when objects are buried.
ï‚· Adjust the sensitivity and discrimination until the metal detector registers the proper type
of metal for each object.
ï‚· Repeat the process until the metal detector accurately detects each coin or type of metal.
Calibration and subsequent validation should be completed before each time you go out with the
metal detector to ensure that the detector is functioning properly. Make sure to adjust the
sensitivity and discrimination for the types of metals for which you are searching and for any
environmental factors that could affect the detector’s calibration.
Recreational Metal Detector Brands
There are dozens of different kinds of recreational metal detectors produced by different
manufacturers. Each detector will have different settings, and that will determine the approach to
calibration that is necessary. These are the top-rated metal detectors from Amazon reviews.
Garrett Ace 300 & 400
Both of these models from Garrett Metal Detectors have high reviews and provide easy
calibration. The 300-level model has only four sensitivity levels, while the 400-level model
doubles that with eight sensitivity levels and depth adjustment.
Additionally, both of these models have five search modes that discriminate between the types of
metals or objects that you hope to find. The main difference between the models is the level of
sensitivity adjustment possible and the size of the search coil.
Digging Deeper: Garrett Ace 300 Review (2020) – Extras Included
Fisher F75


The Fisher F75 line of metal detectors is an affordable favorite. The discrimination accuracy of
these detectors is great for iron-heavy areas and can easily filter out the noise of unwanted
targets. The Digital Shielding Technology that these Fisher models offer reduces electromagnetic
interference and unwanted signals with minimum calibration.
The base frequency at which the Fisher F75 operates is 13 kHz, which will find a wide variety of
targets. This model also has frequency shifting available, which allows for slight changes and
more in-depth calibration options.
Bounty Hunter Tracker IV

The Tracker IV model from Bounty Hunter metal detectors has great sensitivity and
discrimination controls at an affordable price. The tracker is beloved for its ground balancing
capability, which allows it to operate well with any type of sand or soil.
This metal detector has a rugged design that is good for all conditions and can detect larger
objects at up to 3ft depths. It features an 8in coil and operates at a 6.7 kHz frequency.
Teknetics EuroTek Pro

Boasting ultimate calibration control at an affordable price, the EuroTek Pro from Teknetics is
affordable has an impressive battery life for hours of detecting between charges and offers
superior distinction settings for iron.
This model operates at 7.8 kHz and has an 8-inch coil. The 10-level sensitivity settings and a
wide range of discrimination adjustments allows the user to be in control of the experience.
Conclusion – Metal Detector Calibration
So there you have it metal detector calibration. How to do it and why it is important. I hope I provided you with enough information that you were looking for. If you have any questions or comments please leave them below. Thanks for reading and Happy Treasure Hunting!
Thank you. This was very helpful. I’m just getting into metal detectors.
You are very welcome Dennis! You can also check out my Beginners Guide to Metal Detecting for more helpful tips and information on getting started in the metal detecting hobby. Happy treasure hunting!